The Counter-Reformation ( Latin: Contrareformatio ), also sometimes called the Catholic Revival, [1] was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to, and as an alternative to, the Protestant Reformations at the time.
Counter-Reformation | Definition, Summary, Outcomes, Jesuits, Facts, & Significance | Britannica
The Reformation. The Protestant Reformation was the 16th-century religious, political, intellectual and cultural upheaval that splintered Catholic Europe, setting in place the structures and

Source Image: mapleseed.wordpress.com
Download Image
In art history, the 16th century sees the styles we call the High Renaissance followed by Mannerism, and—at the end of the century—the emergence of the Baroque style.Naturally, these styles are all shaped by historical forces, the most significant being the Protestant Reformation’s successful challenge to the spiritual and political power of the Church in Rome.

Source Image: brewminate.com
Download Image
7.11: Reformation and Counter-Reformation – Humanities LibreTexts
The Counter-Reformation was a movement within the Catholic Church to reform itself in the wake of the Protestant Reformation. The term, “Counter-Reformation,” was still unknown in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries and was coined later by non-Catholic historians to denote a Catholic reaction to the Reformation.

Source Image: licensestorehouse.com
Download Image
The Counter Reformation Was A Religious And Political Movement That
The Counter-Reformation was a movement within the Catholic Church to reform itself in the wake of the Protestant Reformation. The term, “Counter-Reformation,” was still unknown in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries and was coined later by non-Catholic historians to denote a Catholic reaction to the Reformation.
By ThoughtCo Updated on June 25, 2019 The Counter-Reformation was a period of spiritual, moral, and intellectual revival in the Catholic Church in the 16th and 17th centuries, usually dated from 1545 (the opening of the Council of Trent) to 1648 (the end of the Thirty Years’ War).
Counter Reformation Collection of Licensed Images, Artwork and Photos #7
Reformation and Counter-Reformation In a sense, the Reformation was a protest against the secular values of the Renaissance. No Italian despots better represented the profligacy, the materialism, and the intellectual hedonism that accompanied these values than did the three Renaissance popes, Alexander VI, Julius II, and Leo X.
Peter Paul Rubens: Weaving a Narrative

Source Image: artandantiquesmag.com
Download Image
What Was the Counter-Reformation in the Catholic Church?
Reformation and Counter-Reformation In a sense, the Reformation was a protest against the secular values of the Renaissance. No Italian despots better represented the profligacy, the materialism, and the intellectual hedonism that accompanied these values than did the three Renaissance popes, Alexander VI, Julius II, and Leo X.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/council-of-trent-fresco-by-brothers-taddeo-and-federico-zuccari-in-hall-of-farnesina-magnificience-of-palazzo-farnese-caprarola-italy-1560-1566-158648764-58b609945f9b5860465205f1.jpg)
Source Image: learnreligions.com
Download Image
Counter-Reformation | Definition, Summary, Outcomes, Jesuits, Facts, & Significance | Britannica
The Counter-Reformation ( Latin: Contrareformatio ), also sometimes called the Catholic Revival, [1] was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to, and as an alternative to, the Protestant Reformations at the time.

Source Image: britannica.com
Download Image
7.11: Reformation and Counter-Reformation – Humanities LibreTexts
In art history, the 16th century sees the styles we call the High Renaissance followed by Mannerism, and—at the end of the century—the emergence of the Baroque style.Naturally, these styles are all shaped by historical forces, the most significant being the Protestant Reformation’s successful challenge to the spiritual and political power of the Church in Rome.

Source Image: human.libretexts.org
Download Image
Why was the Protestant Reformation more successful in some European countries than others? – Quora
Counter-Reformation, or Catholic Reformation, In Roman Catholicism, efforts in the 16th and early 17th centuries to oppose the Protestant Reformation and reform the Catholic church. Early efforts grew out of criticism of the worldliness and corruption of the papacy and clergy during the Renaissance.

Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
The Counter-Reformation and Religious Tensions – German Culture
The Counter-Reformation was a movement within the Catholic Church to reform itself in the wake of the Protestant Reformation. The term, “Counter-Reformation,” was still unknown in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries and was coined later by non-Catholic historians to denote a Catholic reaction to the Reformation.
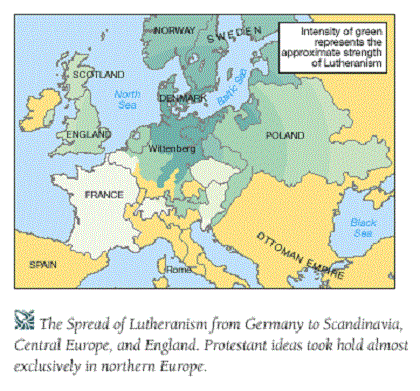
Source Image: germanculture.com.ua
Download Image
Counter-Reformation – Wikipedia
By ThoughtCo Updated on June 25, 2019 The Counter-Reformation was a period of spiritual, moral, and intellectual revival in the Catholic Church in the 16th and 17th centuries, usually dated from 1545 (the opening of the Council of Trent) to 1648 (the end of the Thirty Years’ War).

Source Image: en.wikipedia.org
Download Image
What Was the Counter-Reformation in the Catholic Church?
Counter-Reformation – Wikipedia
The Reformation. The Protestant Reformation was the 16th-century religious, political, intellectual and cultural upheaval that splintered Catholic Europe, setting in place the structures and
7.11: Reformation and Counter-Reformation – Humanities LibreTexts The Counter-Reformation and Religious Tensions – German Culture
Counter-Reformation, or Catholic Reformation, In Roman Catholicism, efforts in the 16th and early 17th centuries to oppose the Protestant Reformation and reform the Catholic church. Early efforts grew out of criticism of the worldliness and corruption of the papacy and clergy during the Renaissance.